
Decoding will recognize and ignore newlines, carriage returns, tabs, and spaces.To divide long output, a newline is added after every 76 characters.

If the final group is not complete, it is padded with '=' characters to make up a length of four.
 Encoding output is made up of groups of four printable characters, with each three bytes of data encoded using four characters. The following are used by MariaDB and MySQL: There are a numerous different methods to base-64 encode a string. The reverse function, FROM_BASE64(), decodes an encoded base-64 string. A NULL argument will return a NULL result. The argument str will be converted to string first if it is not a string. While the resulting strings are larger, using base 64 encoding is a reliable way to ensure that a transmission of binary information is never “misinterpreted.Converts the string argument str to its base-64 encoded form, returning the result as a character string in the connection character set and collation. Whether you’re sending an email, or trying to encode binary streams (images, videos, etc.), base 64 can be seen in many applications. This leaves us with three 6-bit binary groups:Ĭonverting this back to 8-bit groups, we get (the last two zeroes can be ignored): Using the result from the previous section (“aGk=”), we will use the same Base 64 lookup table: Decoding Base64ĭecoding base64 strings follows a similar process, just in reverse. following values to specify the RFC standard to follow for formatting Base64-encoded text. As such, our string “hi” only has 2 characters this means that we need to insert a “=” at the end of the string to make this a valid base 64 string. Returns data as text in the specified Base64 format. We get the following ASCII characters for our string’s binary representation:īefore we can finish off the conversion process, it is important to notice the missing padding: base 64 strings must be groups of 3 characters (6 byte binary representations). Base64 is a way to encode binary data into an ASCII character set known to pretty much every computer system, in order to transmit the data without loss or modification of the contents itself. With the binary representation of our string, we can then make use of an ASCII lookup table above. Now, divide the binary representation into 6-bit groups: We need to convert the ASCII string to its binary representation:Ġ1101000 01101001 ( 0110100001101001 without spaces) Suppose we have “hi” as our string, the ASCII equivalent being: 104 ( h), 105 ( i). For example, mail systems cannot deal with binary data because they expect ASCII (textual) data. The result is an ASCII-readable string that can be safely transmitted and received.įor the sake of simplicity, we’ll use a short string to demonstrate the encoding process. Base64 is a way to encode binary data into an ASCII character set known to pretty much every computer system, in order to transmit the data without loss or modification of the contents itself. Starting with binary information, base 64 splits a binary string into 6-bit groups (note: each zero or one in a binary string is one bit) of three bytes. Java, Python, JS) include built-in functions to facilitate the conversion of base64 encoded information and binary data, the algorithm used to perform the conversion is relatively simple.
Encoding output is made up of groups of four printable characters, with each three bytes of data encoded using four characters. The following are used by MariaDB and MySQL: There are a numerous different methods to base-64 encode a string. The reverse function, FROM_BASE64(), decodes an encoded base-64 string. A NULL argument will return a NULL result. The argument str will be converted to string first if it is not a string. While the resulting strings are larger, using base 64 encoding is a reliable way to ensure that a transmission of binary information is never “misinterpreted.Converts the string argument str to its base-64 encoded form, returning the result as a character string in the connection character set and collation. Whether you’re sending an email, or trying to encode binary streams (images, videos, etc.), base 64 can be seen in many applications. This leaves us with three 6-bit binary groups:Ĭonverting this back to 8-bit groups, we get (the last two zeroes can be ignored): Using the result from the previous section (“aGk=”), we will use the same Base 64 lookup table: Decoding Base64ĭecoding base64 strings follows a similar process, just in reverse. following values to specify the RFC standard to follow for formatting Base64-encoded text. As such, our string “hi” only has 2 characters this means that we need to insert a “=” at the end of the string to make this a valid base 64 string. Returns data as text in the specified Base64 format. We get the following ASCII characters for our string’s binary representation:īefore we can finish off the conversion process, it is important to notice the missing padding: base 64 strings must be groups of 3 characters (6 byte binary representations). Base64 is a way to encode binary data into an ASCII character set known to pretty much every computer system, in order to transmit the data without loss or modification of the contents itself. With the binary representation of our string, we can then make use of an ASCII lookup table above. Now, divide the binary representation into 6-bit groups: We need to convert the ASCII string to its binary representation:Ġ1101000 01101001 ( 0110100001101001 without spaces) Suppose we have “hi” as our string, the ASCII equivalent being: 104 ( h), 105 ( i). For example, mail systems cannot deal with binary data because they expect ASCII (textual) data. The result is an ASCII-readable string that can be safely transmitted and received.įor the sake of simplicity, we’ll use a short string to demonstrate the encoding process. Base64 is a way to encode binary data into an ASCII character set known to pretty much every computer system, in order to transmit the data without loss or modification of the contents itself. Starting with binary information, base 64 splits a binary string into 6-bit groups (note: each zero or one in a binary string is one bit) of three bytes. Java, Python, JS) include built-in functions to facilitate the conversion of base64 encoded information and binary data, the algorithm used to perform the conversion is relatively simple. 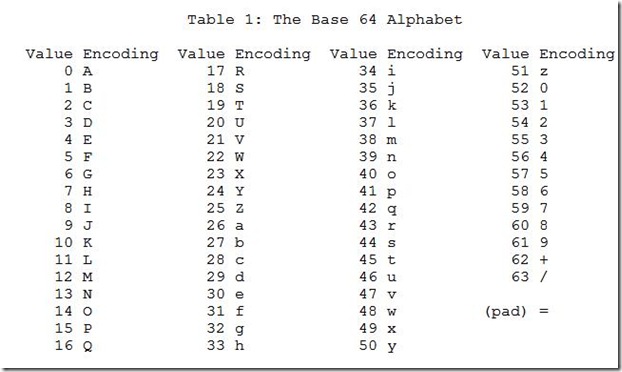
On top of being used for safely encoding image/media data (you may have seen images on the web encoded in the following format: data:image/png base64,(.)), it is used for SSL certificates, email transmissions, and virtually any transfer of information that requires special (control) characters to be escaped. In other words, any base-64 string can be decoded, as long as the string was encoded using a standard set of characters (which the decoder can also understand). Another important distinction is that base 64 does not encrypt any information - it uses a “standard” table of characters to encode and decode information. On base 64 encoded data, the resultant string is always larger than the original (i.e. It achieves this through the conversion of binary data and a “lookup table” - data is eventually made in a stream of ASCII characters, which can then be transmitted and decoded. Base64 encoding is a format designed to prevent communication “mishaps” during the transfer of binary information.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
